Concentration Terminology
Concentration of solution is defined as the amount of solute dissolved in a specific (fixed) amount of solvent.
Contents
Qualitative Description
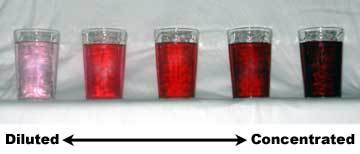
Often, concentration of solution is described qualitatively, through the use of such words as dilute and concentrated. These are relative terms.
Suppose we have \(3\) solutions: \(A,B,\) and \(C\) with \(20\text{ ml},30\text{ ml},\) and \(50\text{ ml}\) alcohol in \(100\text{ ml}\) of water each, respectively. In this case, \(B\) is more dilute than \(C\) while it is more concentrated than \(A\). A solution can be diluted by adding solvent or removing solute. On the other hand, a solution can be concentrated by adding solute or removing solvent.
 Source: Wikipedia, No copyright infringement intended
Source: Wikipedia, No copyright infringement intended
Quantitative Description
Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution:
\[(\text{Molarity})=\frac{(\text{Number of moles of solute})}{(\text{Number of litres of solution})}.\]
It is generally represented by \(\text{M}\). \(_\square\)
\(3.7\text{ g}~\ce{Ca(OH)2}\) is dissolved in \(250\text{ ml}\) of solution. What is its molarity?
The molar mass of \(\ce{Ca(OH)2}\) is \(40+32+2=74\text{ g}\). So the number of moles is obtained as follows:
\[(\text{Number of moles})=\frac{(\text{Given weight})}{(\text{Molar mass})}=\frac{3.7}{74}=0.05.\]
Now, \(250\text{ ml}=0.25\text{ L}\). Hence the molarity is \(\frac{0.05}{0.25}=0.2\text{ M}.\ _\square\)
We have mixed two glucose solution: \(500\text{ ml}\) of \(0.4\text{ M}\) and \(800\text{ ml}\) of \(0.25\text{ M}\). What is the molarity of the final solution formed after mixing these two solutions?
We know that \((\text{Number of moles of solute}) = (\text{Molarity}) \times (\text{Volume of solution}).\)
In the first solution, we have \(\frac{500}{1000} \times 0.4 = 0.2\text{ mol}.\)
In the second solution, we have \(\frac{800}{1000} \times 0.25 = 0.2\text{ mol}.\)
When two solutions are mixed, they will have a total of \(0.2 + 0.2 = 0.4\text{ mol}\) of glucose, and the final volume is \(1.3\text{ L}\). So the final molarity is \(\frac{0.4}{1.3} = \frac{4}{13} \text{ M}.\) \(_\square\)
A \(0.750\text{ M}\) solution of sulfuric acid \(\ce{H2SO4}\) has a density of \(1.046\) grams per milliliter at \(20^\circ\text{C}.\) What is the molality of the solution?
To simplify the problem, assume you have exactly \(1\text{ L}\) of solution. Then you have
\[\begin{align} (\text{Moles of }\ce{H2SO4}) &=(\text{Molarity})\times(\text{Volume})\\ &=0.75\times 1=0.75\\\\ (\text{Mass of solution}) &=(\text{Density})\times(\text{Volume})\\ &=1.046\times 1000=1046\text{ (g)}\\\\ (\text{Mass of solute}) &=(\text{Molar Mass})\times(\text{Number of moles})\\ &=98\times 0.75=73.5\text{ (g)}\\\\ (\text{Mass of solvent}) &=(\text{Mass of solution})-(\text{Mass of solute})\\ &=1046-73.5=972.5\text{ (g)}=0.9725\text{ (kg)}\\\\ (\text{Molality}) &=\dfrac{(\text{Moles of solute})}{(\text{Mass of solvent})}\\ &=\dfrac{0.75}{0.9725}=0.771\text{ (M)}.\ _\square \end{align}\]
Find the molality of 4 molar aqueous pure nitric acid solution. Consider that the density of the solution is \(1\text{ gm/ml}\) for the sake of this question.
Normality is defined as the number of gram equivalents per liter of solution:
\[(\text{Normality})=\frac{(\text{Number of gram equivalents})}{(\text{Number of litres of solution})}.\]
It is generally represented by \(\text{N}.\)
Molarity can be converted to normality by multiplying by valency factor:
\[(\text{Normality)=(Valency Factor})\times(\text{Molarity}).\ _\square\]
What is the normality of a \(0.5\text{ M} \; \ce{H2SO4} \) solution?
The \(n\)-factor of \(\ce{H2SO4} \) is \(2\) since sulphuric acid has two replaceable \(\ce{H+}\) ions.
Since \((\text{Normality}) = (n\text{-factor}) \times (\text{Molarity}),\) the normality is
\[0.5 \times 2 = 1\text{ N}. \ _\square\]
In a beaker containing 2 liters of 3 normal solution of pure sodium hydroxide, how much hydrochloric acid of the same volume must be added to neutralize all of sodium hydroxide contained in it?
Submit your answer in grams (g).
Mole fraction for a component is defined as the number of moles of that component per mole of mixture. In a mixture of \(p\) components, the mole fraction of the \(k^\text{th}\) component is given by \[x_k=\frac{n_k}{n_1+n_2+n_3+\dots+n_p},\] where \(n_a\) represents the number of moles of component \(a\). \(_\square\)
An aqueous solution weighing 100 gram has 60 gram of pure chalk. Then find the mole fraction of the chalk.
If the answer can be expressed as \(\frac{a}{b}\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are coprime positive integers, then submit the value of \(a + b\).
Formality is defined as the number of moles of formula units in one liter of solution. It is used for ionic compounds only: \[(\text{Formality})=\frac{W\times1000}{(\text{GFM})\times[\text{Volume of solution (ml)}]},\] where GFM stands for gram formula mass. \(_\square\)
Percentage weight by weight is defined as \[\frac{(\text{Mass of solute})}{(\text{Mass of solution})}\times100. \ _\square\]
Percentage weight by volume is defined as \[\frac{[\text{Mass of solute (g)}]}{[\text{Volume of solution (ml)}]}\times100.\ _\square\]
Percentage volume by volume is defined as \[\frac{(\text{Volume of solute})}{(\text{Volume of solution})}\times 100.\ _\square\]
Find the molarity of aqueous solution of pure hydrochloric acid which is \(15\)% volume-by-volume.
\[\] Details and Assumptions:
- \(\text{Density of solution} = 2\text{ gm/ml}.\)
- \(\text{Density of solute} = 1.5\text{ gm/ml}.\)
Parts per million (PPM) is defined as
\[\frac{(\text{Mass of solute})}{(\text{Mass of solution})}\times10^6.\]
As this concentration unit is generally used for solutions in which the mass of solute is very small as compared to the mass of solution, we can say that this concentration unit is the same as
\[\frac{(\text{Mass of solute})}{(\text{Mass of solvent})}\times 10^6.\ _\square\]
Relation between the Concentration Terms
We will take mass of solute to be \(m_a\), mass of solvent \(m_{b}\), density of solution \(d\), molecular mass of solute \(M_a\), and molecular mass of solvent \(M_b\)
So we know that
- \(m_b\) g of solute is present in \(m_a \) g of solvent, and
- \(\dfrac{m_b}{m_a}\) g of solute is present in 1 g of solvent,
which implies \( \dfrac{1000m_b}{m_a}\) g of solute in 1000 g of solvent.
So, \(\boxed{\text{Molality}(m)= \dfrac{\dfrac{1000m_b}{m_a}}{M_b} \implies \dfrac{1000m_b}{m_a \times M_b}}.\)
Now, say, assume
- \(m_b\) g of solute in \(m_a+m_b\) g of solution
- \(m_b\) g of solute in \(\dfrac{m_a+m_b}{d}\) ml of solution.
Then we have \(\dfrac{1000 m_b \times d}{m_a+m_b}\) in 1 L of solution, which implies \(\boxed{\text{Molarity}(M)= \dfrac{\dfrac{1000 m_b \times d}{m_a+m_b}}{M_b}}.\)
So \(\boxed{\dfrac{\text{Molality}}{\text{Molarity}} = \dfrac{m_a+m_b}{d\times m_a}}.\)
Here we get the relation guys with derivation. For instance, take the relation between normality (N) and molarity (M) to be
\[\boxed{\text{Molarity} \times n\text{-factor}= \text{Normality}}.\ _\square\]
Dependence on Volume/Temperature
Some of the concentration terms depend on the volume of solution/solvent like molarity and normality. The volume changes as the temperature is varied. Thus, such concentration terms are temperature dependent. On the other hand, terms like molality and mole fraction do not depend on volume, thus being temperature independent. The density is often required to convert temperature independent terms into temperature dependent terms or vice versa.