Angles
An angle is a geometric shape formed by the intersection of two line segments, lines, or rays. Angles are a measure of rotational distance as contrasted with linear distance. An angle can also be thought of as a fraction of a circle. The angle between the two line segments is the distance (measured in degrees or radians) that one segment must be rotated around the intersecting point so that the two segments overlap. Angles are important to defining and studying polygons such as triangles and quadrilaterals. They are used in a variety of disciplines, ranging from animation to carpentry to physics.
Contents
Types of Angles
Angles can be classified into five groups, based on their measure in degrees.

- Acute: angles with measure \( < 90^\circ \)
- Right: angles with measure \( = 90^\circ \)
- Obtuse: angles with measure \( > 90^\circ \) and \( < 180 ^ \circ \)
- Straight: angles with measure \( = 180^ \circ \)
- Reflex: angles with measure \( > 180^ \circ \) and \( < 360 ^ \circ \)
If \( \angle ABC = 99^ \circ \), what type of angle is it?
Since \( 90^ \circ < 99 ^ \circ < 180^ \circ \), angle ABC is an obtuse angle. \(_\square\)
If angle \(XYZ \) is acute, which of the following is a possible measure of it?
\(\quad \text{A)}\) \( 23 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{B)}\) \( 90 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{C)}\) \( 123 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{D)}\) \( 180 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{E)}\) \( 190 ^ \circ \)The answer is \(\text{A}. \) An acute angle is between \(0^ \circ \) and \( 90^ \circ \). The only value that lies within this range is \( 23 ^ \circ .\) \(_\square\)
For the graphic above, which of the angles below is an acute angle?
\(\quad \text{A) } AOD\)
\(\quad \text{B) } COA\)
\(\quad \text{C) } BOC\)
\(\quad \text{D) } DOB\)The answer is \(\text{C}.\) \( AOD \) is a straight angle. Both \( COA\) and \(DOB\) are obtuse. Only \(BOC\) is less than \( 90^\circ,\) so it is the only acute angle in the list. \(_\square\)
If \(\angle ABC\) is obtuse and \( \angle ABC = 2 \angle DEF \), what type of angle is \(DEF?\)
Since \( \angle ABC \) is obtuse, it follows that \( 90^ \circ < \angle ABC < 180^ \circ \). Similarly, if \( \angle DEF = \frac{ \angle ABC } { 2} \), then \( 45^ \circ < \angle DEF < 90 ^ \circ \). Therefore, \( \angle DEF \) is an acute angle. \(_\square\)
If \( \angle AOB \) is acute and \( \angle BOC \) is acute, and the points \(A\) and \(C\) lie on opposite sides of the line \(BO\), what is known about the angle \(AOC? \)
\(\quad \text{A) }\) \( 0 ^ \circ < \angle AOC < 90 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{B) }\) \( 0 ^ \circ < \angle AOC < 180 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{C) }\) \( 90 ^ \circ < \angle AOC < 180 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{D) }\) \( 90 ^ \circ < \angle AOC < 360 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{E) }\) \( 180 ^ \circ < \angle AOC < 360 ^ \circ \)\( \angle AOB \) and \( \angle BOC \) are acute, which means that \( 0 ^ \circ < \angle AOB < 90 ^ \circ \) and \( 0 ^ \circ < \angle BOC < 90 ^ \circ \). Since points \(A\) and \(C\) lie on opposite sides of the line \(BC\), we have \( \angle AOC = \angle AOB + \angle BOC \).Therefore: \( 0 ^ \circ < \angle AOC < 90^\circ + 90^ \circ = 180^ \circ \) and the answer is \(\text{B}.\) \(_\square\)
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Complementary angles are angles that add together to make a right angle. That is, \(\angle X\) and \(\angle Y\) are complementary if \(\angle X + \angle Y = 90^\circ.\)
Supplementary angles are angles that add together to make a straight line. That is, \(\angle X\) and \(\angle Y\) are supplementary if \(\angle X + \angle Y = 180^\circ.\)
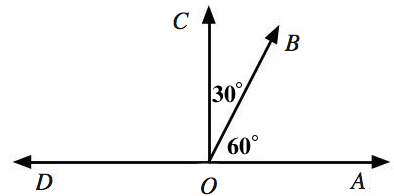
In the image above, \( \angle AOB \) and \( \angle BOC \) are complementary, and \( \angle DOB \) and \( \angle BOA \) are supplementary.
Angles \( AOB \) and \(BOC\) are complementary. What is the measure of angle \( AOC? \)
Since the two angles are complementary, their sum is \( 90^\circ \). Therefore, \( \angle AOC = \angle AOB + \angle BOC = 90 ^ \circ.\ _\square \)
Three points \(X, Y, Z\) lie on a straight line in that order. What can we say about angles \( XYO\) and \( OYZ,\) where \(O\) does not lie on the line?
Since the points lie on a straight line, \( \angle XYO + \angle OYZ = 180 ^ \circ \), these angles are supplementary. \(_\square\)
If \( \angle P = 23 ^ \circ \), which of the following is complementary to it?
\(\quad \text{A) }\) \(23^\circ \)
\(\quad \text{B) }\) \( 67^\circ \)
\(\quad \text{C) }\) \( 77 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{D) }\) \( 113 ^ \circ \)
\(\quad \text{E) }\) \( 157 ^ \circ \)
The complementary angles would add together to give \( 90 ^ \circ \), so we have \( 90 ^ \circ - 23 ^ \circ = 67 ^ \circ, \) implying that the answer is \(\text{B)}. \) \(_\square\)
What is the sum of the complementary angles?
If \(\angle A \) and \(\angle B \) are supplementary, and \( \angle A - \angle B = 40 ^ \circ \), what are the measures of angles \(A\) and \(B?\)
Given that \( \angle A + \angle B = 180 ^ \circ \) and \( \angle A - \angle B = 40 ^ \circ \), solve the system of equations. Adding the two yields \( 2 \angle A = 220 ^ \circ \), or \( \angle A = 110 ^ \circ \). Finally, \( \angle B = 180 ^ \circ - 110 ^ \circ = 70 ^ \circ \). \(_\square\)
If angles \(X\) and \(Y\) are complementary, and angles \(Y\) and \(Z\) are supplementary, what do we know about angles \(X\) and \(Z?\)
We have \( X + Y = 90 ^ \circ \) and \( Y + Z = 180 ^ \circ \).Therefore, \( Z - X = (Z+Y) - (X+Y) = 180 ^ \circ - 90 ^ \circ = 90 ^ \circ \). \(_\square\)
The magnitude of the complementary of an angle is equal to the square of the angle's magnitude.
Find the angle in degrees.
Vertical Angles
The two opposite angles formed by a pair of intersecting lines are called vertical angles. These angles have equal measures.
\(\hspace{5cm}\)
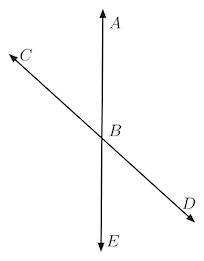
In the diagram above \( \angle ABC \) and \( \angle DBE \) are vertical angles and are therefore equal.
If lines \( PQ\) and \(XY\) intersect at \(O\), which angle is vertically opposite \( \angle POX?\)
The angle that is vertically opposite \( \angle POX\) will be \( \angle QOY\) \((\)which is also \( \angle YOQ). \) \(_\square\)
In the following diagram, which pair of angles are vertically opposite?
\(\quad \text{A) }\) \( ABC, CBI\)
\(\quad \text{B) }\) \( ABH, HBJ \)
\(\quad \text{C) }\) \( HBJ, JBI \)
\(\quad \text{D) }\) \( ABC, HBI \)
\(\quad \text{E) }\) \( ABH, JBI \)\(\hspace{5cm}\)
 Working through these pairs, we see that the only pair of opposite angles are \(ABC\) and \(HBI \). Therefore, the answer is \(\text{D)}\). \(_\square\)
Working through these pairs, we see that the only pair of opposite angles are \(ABC\) and \(HBI \). Therefore, the answer is \(\text{D)}\). \(_\square\)Note: Another pair of vertical angles are \(ABH\) and \(CBI\).
Given that \(ABE \) and \(CBD\) are straight lines intersecting each other, if \( \angle ABD = 75 ^ \circ \), what is the measure of \( \angle CBE?\)
\(\hspace{5cm}\)

\( \angle CBE\) and \( \angle ABD\) are vertical angles, and thus \( \angle CBE = \angle ABD = 75 ^ \circ \). \(_\square\)
If \( \angle AOB \) and \( \angle COD \) are vertically opposite angles and \( \angle AOB + \angle COD = 90 ^ \circ \), what is the measure of \( \angle AOB?\)
Since they are vertically opposite angles, \( \angle AOB = \angle COD \). Therefore, \( 2 \angle AOB = 90 ^ \circ \), or \( \angle AOB = \frac{ 90^ \circ } { 2} = 45 ^ \circ \). \(_\square\)
In the following diagram, given that \( ABC = 80^\circ \) and \( HBJ= 35^\circ \), what is the measure of \( JBI?\)
\(\hspace{6cm}\)
 Since \( ABC \) and \( HBI \) are vertical angles, they are equal. Thus, \( ABC = HBI = 80^\circ \). But \( HBI = HBJ + JBI \). Thus \( 80^\circ = 35^\circ + JBI \). Therefore, \( JBI = 45^\circ \). \(_\square\)
Since \( ABC \) and \( HBI \) are vertical angles, they are equal. Thus, \( ABC = HBI = 80^\circ \). But \( HBI = HBJ + JBI \). Thus \( 80^\circ = 35^\circ + JBI \). Therefore, \( JBI = 45^\circ \). \(_\square\)

In the figure, with \( \angle BAC = 40 ^ \circ,\) what is the measure of \( \angle ABC \) (in degrees)?
\(\)
Clarification: \(HFAC, DFG, EDCB, IHGJ\) are all straight lines.

Three line segments \(AD, BE, CF\) intersect at a single point in the diagram at right.
Find the sum of the angles \(a+b+c+d+e+f\) in degrees.
Angle Chasing
It is possible to find a missing angle measure if the values of other angles in the question are known. Start by drawing a diagram and labeling each known angle.
- Angles at a point sum to \( 360 ^ \circ \).
- Angles on a line sum to \( 180 ^ \circ \).
- Angles in a triangle sum to \( 180 ^ \circ \).
- Vertical angles are equal.
\(A, B\) and \(C\) are 3 consecutive points on a line. If \( \angle ABX = 35 ^ \circ \), what is the measure of \( \angle CBX?\)
Angles on a line sum to \( 180 ^ \circ \), so we have \( \angle ABX + \angle CBX = 180 ^ \circ \). Hence, this gives us \( \angle CBX = 180 ^ \circ - \angle ABX = 145 ^ \circ \). \(_\square\)
Lines \(AB\) and \(CD\) intersect at \( O \). If \( \angle AOD = 70 ^ \circ \), what is the measure of angle \( BOD?\)
Since \(AOD \) and \(BOD\) are angles on the line \(\text{A-O-B}\), they sum up to \( 180 ^ \circ \). Thus\[ \angle BOD = 180^ \circ - 70 ^ \circ = 110^ \circ.\ _\square \]
In the following image, if \( \angle ADB = 20 ^ \circ \) and \( \angle ADC = 50 ^ \circ \), what is the measure of angle \( BDC?\)
image
We have \( \angle BDC = \angle ADC - \angle ADB = 50 ^ \circ - 20 ^ \circ = 30 ^ \circ \). \(_\square\)
 Find the value of \(x.\)
Find the value of \(x.\)
Note: \(ACD\) is a straight line.
 In the figure, what is the measure of \(\angle BKM\) (in degrees)?
In the figure, what is the measure of \(\angle BKM\) (in degrees)?
Remembering that the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is \(180^\circ\) is useful in solving the following examples:
In triangle \(ABC\), if \( \angle ABC = 40 ^ \circ \) and \( \angle BCA = 60 ^ \circ \), what is the measure of angle \( CAB?\)
 Since angles in a triangle sum to \( 180 ^ \circ \),
Since angles in a triangle sum to \( 180 ^ \circ \),\[ \angle CAB = 180 ^ \circ - \angle ABC - \angle BCA = 180^ \circ - 40 ^ \circ - 60 ^ \circ = 80 ^ \circ . \ _\square \]

Find the sum (in degrees) of the four colored angles in the diagram.

In the figure, four line segments \(AB, CD, EF, GH\) intersect at a single point.
Find the value (in degrees) of the angle sum \(x + y + w + z.\)
\(\)
Note: \(\angle EFH = 55 ^ \circ\), \(\angle ACD = 37 ^ \circ\), and \(\angle GHF = 85 ^ \circ\).
